Egypt: Reform unjust vice laws, guarantee open civic space
During Egypt's UPR adoption at HRC59, Nora Noralla delivered a joint statement on behalf of ISHR, Cairo 52 and Middle East Democracy Center. Watch and read the full statement below.
©Free Huang XueQin & Wang JianBing

The Chinese authorities weaponise laws to target dissidents in the name of ‘national security’: journalists are no exception. On World Press Freedom Day, ISHR calls on the authorities to release independent journalist Huang Xueqin and her friend, labour rights activist Wang Jianbing. Both were unjustly held for 226 days.
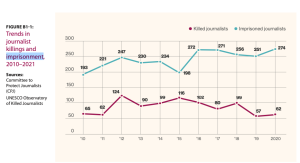
As the international community marks World Press Freedom Day on 3 May, a recent report released by UNESCO highlights patterns of threats and attacks against journalists worldwide. The report cites Committee to Protect Journalist (CPJ) data on journalists imprisoned from 2010-2021, with more than 190 journalists imprisoned each year, and a ten-year peak of 274 in 2021. Independent Chinese journalist Huang Xueqin is one of them.
On 19 September 2021, #MeToo activist and independent journalist Huang Xueqin and labour rights advocate Wang Jianbing were arrested by the police in the city of Guangzhou, due to weekly private gatherings they convened in Wang’s residence. Both were suspected to be placed under ‘Residential Surveillance at a Designated Location’ (RSDL), a criminal procedure in Chinese law considered by UN experts as ‘a form of enforced disappearance’. It was not until early November 2021 that Huang and Wang’s family members received a ‘notice of arrest’ from the police, which indicated that the duo had been formally arrested on charges of ‘inciting subversion of State power’, and being detained at the Guangzhou No. 1 Detention Center.
Before becoming an independent journalist, Huang Xueqin had worked as an investigative journalist for some mainstream media in China. She focused on issues such as women’s rights, public interest, corruption of Chinese officials, corporate pollution, and marginalized groups. She also participated in many #MeToo campaigns to provide support and assistance to victims of sexual assault and harassment. On 17 October 2019, she was criminally detained by Guangzhou police for publishing articles on the Anti-Extradition Law Amendment Bill Movement in Hong Kong. After 3 months under RSDL, Huang was later released on bail on 17 January 2020. She had received a Chevening Scholarship in 2021, and was planning to leave for the UK on 20 September 2021, the day before her arrest. Wang Jianbing has worked in the non-profit sector for over 16 years. He was engaged in a variety of issues including education, disability, youth and labour. Since 2018, he has devoted to advocacy and service provision for workers with occupational diseases such as pneumoconiosis, providing necessary legal support.
Since their arrest, Guangzhou police, jointly with the public security departments across the country, have interrogated around 70 of Huang and Wang’s friends. In contravention of Chinese criminal procedure provisions, the police interrogated their friends for up to 24 hours, several times for some of them, while searching and copying their electronic devices. The police also threatened and coerced some of Huang and Wang’s friends into false confession by signing fabricated statements, which claimed that they have allegedly participated in training activities with an intention of ‘subverting State power’ and organised ‘political meetings’ to criticise the government.
Meanwhile, Huang Xueqin’s family and family-appointed lawyers have been repeatedly denied access to seeing her, while Wang Jianbing has had one successful meeting with his family-appointed lawyer on 1 April. Wang was reportedly held in solitary confinement for more than five months in a so-called ‘isolation area’ outside the detention center, where he was interrogated several times per day over a long period of time. The exact location is unknown to date. Their conditions of detention remain a cause of concern for their relatives, and they are unable to access funds transferred by the latter ones.
On 3 February 2022, six UN human rights experts wrote a joint letter to the Chinese government expressing ‘serious concern regarding the detention and subsequent enforced disappearance of human rights defenders Wang Jianbing’. The experts underlined that ‘arrests of human rights defenders for carrying out their legitimate work, or the exercise of human rights, under the pretext of national security is incompatible with international human rights law.’ The government has so far not responded.
This is indicative of a broader pattern of growing restrictions on the space for discussion and debate in China, where those who defend and exercise this right find themselves increasingly at risk of medium to long-term incarceration, often under the framework of national security or counter-terrorism legislation.Letter to the Chinese government by six UN independent human rights experts, 3 February 2022.
In an address to High Commissioner Michelle Bachelet at the March 2022 session of the UN Human Rights Council, ISHR condemned Huang Xueqin’s disappearance and the Chinese authorities’ abuse of national security to detain human rights defenders without access to a lawyer, and curtail free speech.
ISHR calls on the Chinese authorities to:
Immediately, and unconditionally, release Huang Xueqin and Wang Jianbing;
Ensure respect for the right to a fair trial and due process guarantees in line with international human rights standards, for all detained individuals;
Immediately repeal the provisions under China’s Criminal Procedure allowing for Residential Surveillance at a Designated Location (RSDL);
Review provisions under national security legislation that contravene international law obligations, including relevant provisions in China’s Criminal Law (Part II, Chapter I) and Criminal Procedure Law (article 24), to bring them in line with international human rights standards.

During Egypt's UPR adoption at HRC59, Nora Noralla delivered a joint statement on behalf of ISHR, Cairo 52 and Middle East Democracy Center. Watch and read the full statement below.

The 59th session of the UN Human Rights Council (16 June to 9 July 2025) will consider issues including civil society space, climate change, sexual orientation and gender identity, violence and discrimination against women and girls, poverty, peaceful assembly and association, and freedom of expression, among others. It will also present an opportunity to address grave human rights situations including in Afghanistan, Belarus, China, Eritrea, Israel and oPt, Sudan, Syria and Venezuela, among many others. Here’s an overview of some of the key issues on the agenda.

On 8 May 2025, during the 83rd ordinary session of the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights (ACHPR), ISHR delivered a statement under Item 5, which focused on the activity report of the Special Rapporteur on Human Rights Defenders. The statement reaffirmed ISHR’s strong commitment to the protection and empowerment of defenders across Africa.